Alot of people are used to knowing just arthritis without the knowledge of chronic issues like Rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. Understanding this condition is crucial for those diagnosed and their loved ones.
Here are 10 key things you need to know about rheumatoid arthritis:
1. Autoimmune Nature
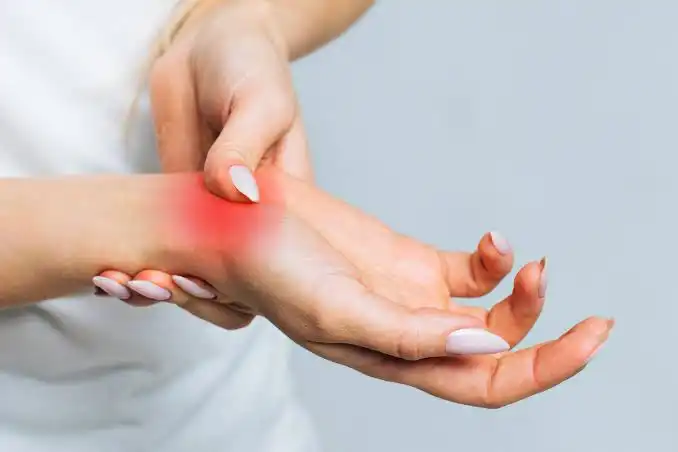
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, meaning the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. In RA, the immune system targets the synovium, the lining of membranes that surround joints.
2. Joint Involvement
RA commonly affects joints on both sides of the body, such as wrists, knees, and fingers. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is often associated with wear and tear, RA impacts joints symmetrically and can lead to deformities over time.
3. Fluctuating Symptoms
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can vary in severity and may come and go. Periods of increased inflammation, known as flares, can be followed by periods of remission. Understanding these fluctuations is essential for managing the condition effectively.
Read Here: 4 Essential Tips for living well with Dementia
4. Early Diagnosis Matters
Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing RA. Timely diagnosis allows for prompt treatment to slow or prevent joint damage. If you suspect RA symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for assessment and diagnosis.
5. Treatment Options
Various medications, including disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologics, are employed to manage RA. These drugs help control symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent joint damage. Physical therapy and lifestyle changes also play a vital role in treatment.
6. Impact Beyond Joints
Rheumatoid arthritis isn’t confined to the joints. It can affect other organs and systems, leading to complications such as cardiovascular problems and lung issues. Regular health check-ups are important to monitor and manage these potential complications.
7. Lifestyle and Diet
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can positively impact RA. Regular exercise helps maintain joint flexibility and reduces stiffness. Additionally, an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, and vegetables may complement medical treatments.
8. Individualized Approach
RA affects individuals differently. What works for one person may not work for another. Personalized treatment plans, developed in consultation with healthcare professionals, are essential for managing the unique challenges posed by RA.