Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer among men, with millions of cases diagnosed worldwide each year. While genetics plays a significant role in the development of this disease, lifestyle and habits can also contribute to your risk.
Here are seven habits that can increase the risk of prostate cancer:
1. Poor Diet
A diet high in saturated fats, processed foods, and red meat has been associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. To lower your risk, focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Tomatoes, which contain lycopene, have been linked to a reduced risk of prostate cancer.
2. Lack of Exercise
A sedentary lifestyle can lead to obesity and increase your risk of prostate cancer. Regular physical activity not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also promotes overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
3. Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for several cancers, including prostate cancer. The harmful chemicals in tobacco can damage DNA and increase the likelihood of cancer development. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk.
4. Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Heavy alcohol consumption has been associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. Moderation is key; limit your alcohol intake to reduce your risk. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation and consider alternatives like red wine, which may have some health benefits.
Read Also: 8 Factors That Can Cause Miscarriage During Pregnancy
5. Chronic Stress
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and promote inflammation, potentially contributing to cancer development. Adopt stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to help manage stress and improve overall health.
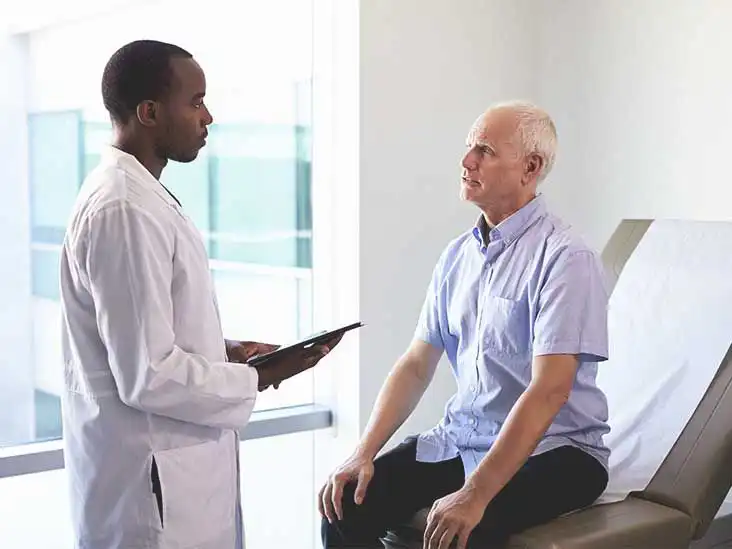
6. Lack of Regular Checkups
Neglecting routine medical checkups can lead to delayed detection of prostate cancer. Regular checkups and screenings can catch cancer in its early stages when it’s more treatable. Discuss with your healthcare provider when and how often you should get screened.
7. Exposure to Environmental Toxins
Exposure to certain environmental toxins and chemicals, such as pesticides and industrial pollutants, may increase the risk of prostate cancer. While it’s challenging to avoid all environmental toxins, you can minimize exposure by using protective gear and being aware of your surroundings.
While prostate cancer is influenced by genetic factors, these seven habits can increase your risk of developing the disease. By making positive lifestyle changes, such as improving your diet, staying physically active, quitting smoking, moderating alcohol consumption, managing stress, scheduling regular checkups, and reducing exposure to environmental toxins, you can lower your risk of prostate cancer.