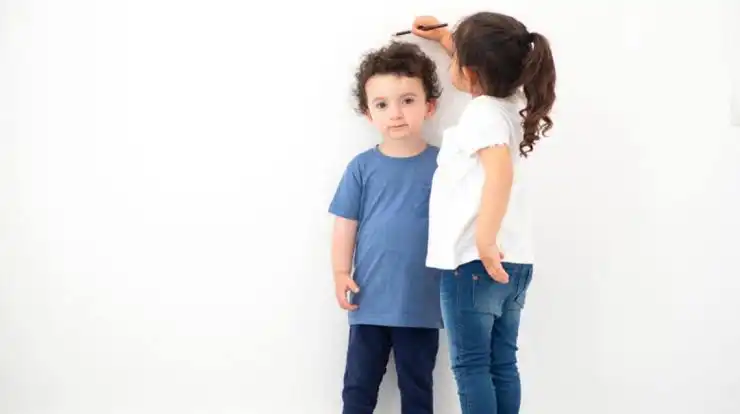
Stunted growth in children can be a cause for concern for parents and caregivers because children are expected to grow at certain stages in their lives. Proper growth and development are crucial during the formative years, and any hindrance to this process can have long-term implications.
Here are five possible reasons why a child might experience stunted growth:
1. Nutritional Deficiencies
One of the primary reasons for stunted growth in children is inadequate nutrition. A lack of essential nutrients such as proteins, vitamins, and minerals can impede the body’s ability to grow and develop properly. Malnutrition during the early years, especially when the body is rapidly growing, can lead to irreversible consequences. It’s essential for children to receive a balanced diet that supports their overall health and development.
2. Genetic Factors
Genetics plays a significant role in determining a child’s growth potential. If parents are shorter in stature, it’s possible that their children may inherit these genetic traits. While genetics can set the stage for a child’s growth, it’s important to note that environmental factors, such as nutrition and healthcare, also play a crucial role. Regular check-ups with pediatricians can help identify any underlying genetic conditions that may affect growth.
Read Here: 8 Key Things to Know About Rheumatoid Arthritis
3. Chronic Illnesses
Chronic illnesses can have a profound impact on a child’s growth. Conditions such as celiac disease, kidney disorders, and hormonal imbalances can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb nutrients or produce growth hormones. Identifying and managing these health issues early on is crucial for ensuring proper growth. Regular medical check-ups and consultations with healthcare professionals are essential for monitoring a child’s overall health.
4. Inadequate Physical Activity
Physical activity is not only crucial for overall health but also for proper growth. Lack of exercise and sedentary lifestyles can contribute to stunted growth. Physical activity stimulates the release of growth hormones and helps in the development of strong bones and muscles. Encouraging children to engage in regular physical activities, such as sports and play, is vital for their overall well-being.
5. Psychosocial Factors
Emotional and psychosocial factors can also influence a child’s growth. Stress, anxiety, and exposure to traumatic events can have a negative impact on overall health and development. Creating a supportive and nurturing environment at home and school is essential for a child’s emotional well-being. Ensuring that a child feels safe, loved, and secure can contribute positively to their growth trajectory.






![Couple caught p@nts down in a public toilet [VIDEO] 10 Couple caught p@nts down in a public toilet [VIDEO]](https://newsblenda.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/IMG_20231011_111108-75x75.webp)